-
Tangki Kaca Yang Dilelehkan Ke Baja (469)
-
Tangki Baja Tidak Berlemak (434)
-
Tangki epoxy yang terikat dengan fusi (469)
-
Tangki Baja Galvanis (321)
-
Atap Dome Aluminium (1257)
-
Tangki penyimpanan air limbah (226)
-
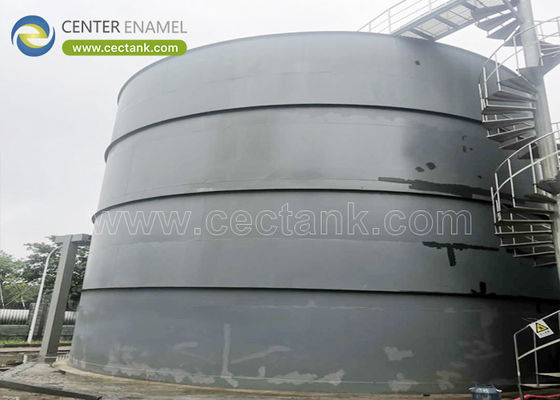
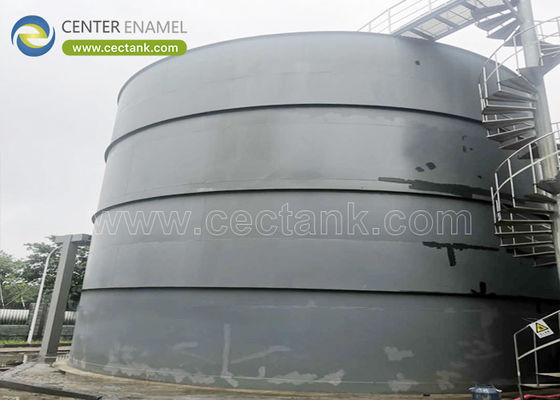
tangki baja las (457)
-
Kapal Tekanan (295)
-
Pencernaan Anaerobik (201)
-
Tangki Air Industri (349)
-
Tangki baja berlapis kaca (180)
-
Tangki Baja Berbolt (345)
-
Tangki Penyimpanan Lumpur (115)
-
Tangki Penyimpanan Biogas (173)
-
Tangki Penyimpanan Leachate (133)
-
Tangki penyimpanan air pertanian (179)
-
Tangki Air Api (166)
-
Silos Gudang Gandum (146)
-
Proyek Biogas (381)
-
Proyek Pengolahan Air Limbah (270)
-
Atap Membran Ganda (223)
Tangki Baja Tahan Karat Las: Solusi Kuat dan Higienis untuk Industri Modern
| Tempat asal: | CINA |
| Nama merek: | CEC TANKS |
| Sertifikasi: | ISO 9001:2008, AWWA D103 , OSHA , BSCI |
| Nomor model: | W |
| Kuantitas min Order: | 1set |
| Harga: | $5000~$20000 one set |
| Kemasan rincian: | Pe poly-foam di antara masing-masing dua pelat baja; palet kayu dan kayu |
| Waktu pengiriman: | 10-30 hari setelah setoran diterima |
| Syarat-syarat pembayaran: | L/c, t/t |
| Menyediakan kemampuan: | 60 set per bulan |
|
Informasi detil |
|||
| Tempat asal | CINA | Nama merek | CEC TANKS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sertifikasi | ISO 9001:2008, AWWA D103 , OSHA , BSCI | Nomor model | W |
| Resistensi korosi: | Cocok untuk air garam air limbah, air laut, minyak mentah sulfur tinggi, rubah garam, senyawa organi | Elastis: | Sama seperti lembaran baja |
| Warna tubuh tangki: | Desain yang disesuaikan | Ketebalan lapisan: | Disesuaikan |
| Dasar: | Konkret | Tingkat baja: | baja tahan karat |
| Menyoroti: | tangki baja tahan karat las,tangki baja sanitasi untuk industri,tangki baja las industri |
||
Deskripsi Produk
Tangki Baja Tahan Karat Las: Solusi Kuat dan Higienis untuk Industri Modern
Sebagai penulis pemasaran global untuk Shijiazhuang Zhengzhong Technology Co., Ltd (Center Enamel), saya menyajikan artikel komprehensif tentang tangki baja tahan karat las. Bejana-bejana ini telah menjadi landasan dalam industri mulai dari makanan dan minuman hingga farmasi, kosmetik, dan pengolahan bahan kimia.
Pendahuluan: Nilai abadi dari tangki baja tahan karat las
Tangki baja tahan karat menawarkan kombinasi menarik antara daya tahan, kebersihan, dan keserbagunaan. Ketika pengelasan digunakan untuk menyambung komponen, produsen mendapatkan sambungan yang kedap bocor, integritas struktural yang kuat, dan interior mulus yang lebih mudah dibersihkan dan disanitasi. Center Enamel mengkhususkan diri dalam tangki baja tahan karat las yang dirancang untuk memenuhi persyaratan industri yang ketat, mulai dari hasil akhir sanitasi hingga ketahanan korosi di lingkungan yang menantang. Hasilnya adalah serangkaian tangki yang dapat mendukung operasi penting seperti fermentasi, penyimpanan, pencampuran, penyaringan, dan proses reaksi.
Keunggulan utama dari tangki baja tahan karat las
- Kemudahan pembersihan dan sanitasi: interior yang halus dan dipoles meminimalkan kekasaran permukaan, mengurangi tempat bersarang mikroba dan menyederhanakan rutinitas pembersihan di tempat (CIP).
- Kekuatan dan daya tahan: sambungan las menyediakan jalur beban yang berkelanjutan, meningkatkan kekuatan mekanik di bawah tekanan, agitasi, atau siklus termal.
- Ketahanan korosi: baja tahan karat dengan kimia paduan yang sesuai tahan terhadap pitting, korosi celah, dan serangan kimia di banyak lingkungan pemrosesan.
- Kustomisasi: opsi desain modular, berbagai konfigurasi bukaan, dan integrasi dengan fitting memungkinkan penyesuaian untuk proses tertentu.
- Umur panjang dan total biaya kepemilikan: daya tahan yang luar biasa menghasilkan biaya siklus hidup yang lebih rendah, lebih sedikit penggantian, dan perawatan yang dapat diprediksi.
Material: memilih baja tahan karat yang tepat
Pemilihan material adalah dasar dari kinerja, kebersihan, dan biaya. Kelas baja tahan karat yang paling umum untuk tangki las adalah paduan austenitik, dengan 304 dan 316 menjadi andalan untuk banyak industri.
- Baja tahan karat 304:
- Manfaat: ketahanan korosi keseluruhan yang baik, kemampuan bentuk yang sangat baik, mudah didapat, hemat biaya.
- Keterbatasan: kurang tahan terhadap lingkungan yang mengandung klorida daripada 316; tidak ideal untuk kondisi yang sangat asam atau asin.
- Baja tahan karat 316:
- Manfaat: ketahanan korosi yang unggul dalam klorida, kinerja yang lebih baik di lingkungan laut atau asin, ketahanan CIP yang sangat baik.
- Keterbatasan: biaya material yang lebih tinggi, kemampuan bentuk yang sedikit lebih rendah daripada 304 dalam beberapa geometri.
- Hasil akhir dan kualitas permukaan:
- Hasil akhir interior: dipoles cermin (316L adalah umum) untuk aplikasi higienis, dengan kekasaran permukaan biasanya Ra ≤ 0,8 μm atau lebih baik untuk kemudahan pembersihan.
- Hasil akhir eksterior: lapisan pelindung atau permukaan yang dipoles untuk ketahanan korosi dan estetika.
- Pasivasi: pasivasi pasca-las untuk meningkatkan ketahanan korosi pada lasan.
Pertimbangan konfigurasi dan desain
- Geometri tangki:
- Silinder dengan ujung datar atau cekung adalah tipikal untuk penyimpanan dan pencampuran.
- Bagian bawah kerucut mendukung drainase lengkap dan pembersihan yang efisien; kerucut yang lebih dangkal digunakan untuk agitasi atau persyaratan tinggi tertentu.
- Desain bagian bawah miring atau V meminimalkan zona mati dan memfasilitasi CIP.
- Ketebalan dinding dan desain cangkang:
- Ketebalan didorong oleh tekanan internal, intensitas agitasi, suhu, dan persyaratan ruang kepala.
- Kepala dan bagian bawah dirancang untuk memastikan integritas struktural dan drainase yang tepat.
- Bukaan dan port:
- Saluran masuk, saluran keluar, keran pengambilan sampel, ventilasi, manway, dan penetrasi instrumen harus diposisikan untuk mengoptimalkan aliran, sanitasi, dan akses.
- Gasket, segel, dan fitting sanitasi (sambungan Tri-Clamp, butt-wused) dipilih untuk meminimalkan celah dan memungkinkan pembersihan yang mudah.
- Agitasi dan pencampuran:
- Interior tangki dapat mencakup penggerak magnetik, agitator masuk atas atau masuk bawah, dengan segel poros berukuran untuk kompatibilitas CIP.
- Baffle dan stiffener dapat meningkatkan efisiensi pencampuran dan mengurangi pusaran.
- Transfer panas dan kontrol suhu:
- Jaket dan koil eksternal atau internal memungkinkan pemanasan atau pendinginan untuk proses yang peka terhadap suhu.
- Desain termal mempertimbangkan koefisien perpindahan panas, sifat fluida, dan kompatibilitas CIP.
- Isolasi dan efisiensi energi:
- Isolasi mengurangi hilangnya panas dalam tangki proses, terutama di lingkungan dingin atau proses panas.
- Isolasi dipilih agar kompatibel dengan persyaratan CIP/SIP dan keselamatan kebakaran.
- Sanitasi dan kebersihan:
- Desain higienis meminimalkan zona mati dan ruang bawah tanah tempat residu dapat menumpuk.
- Lasan digiling dan dipoles, dengan transisi yang halus dan sudut membulat untuk mencegah tempat bersarang mikroba.
- Kepatuhan dan standar:
- Di banyak pasar, tangki harus memenuhi ISO 9001 untuk manajemen mutu, penandaan CE jika berlaku, dan standar khusus sektor (FDA untuk makanan, Standar Sanitasi 3-A untuk produk susu, pedoman EHEDG untuk desain higienis).
Proses manufaktur: dari desain hingga tangki jadi
- Rekayasa dan spesifikasi:
- Klien menyediakan parameter proses, termasuk volume, suhu, tekanan, jenis agitasi, kebutuhan pembersihan, dan batasan ruang.
- Center Enamel menerjemahkan persyaratan menjadi model 3D terperinci, daftar material, dan rencana fabrikasi.
- Persiapan dan pemotongan pelat:
- Lembaran baja tahan karat dipotong sesuai ukuran dengan alat potong presisi, memastikan distorsi minimal dan tepi bebas gerinda.
- Pembentukan dan pembentukan:
- Silinder dan kepala dibentuk melalui teknik penggulungan, pemintalan, atau pembengkokan, tergantung pada geometri.
- Pengelasan dan integritas jahitan:
- Las fillet dan butt menyambung pelat dan kepala. Prosedur pengelasan memenuhi syarat, dan tukang las melakukan sesuai dengan standar kualitas yang ketat.
- Metode pengujian non-destruktif (NDT) seperti inspeksi visual, penetran pewarna, atau radiografi dapat digunakan untuk memastikan kualitas lasan.
- Penyelesaian permukaan:
- Permukaan interior digiling dan dipoles untuk mencapai kekasaran yang diperlukan.
- Permukaan dapat dipasivasi untuk meningkatkan ketahanan korosi, terutama di sekitar lasan dan penetrasi.
- Perakitan dan pemasangan:
- Sambungan baut atau dijepit dengan gasket sanitasi memungkinkan perakitan tanpa mengorbankan kebersihan.
- Lampiran seperti nosel, kaki, atau rangka penyangga diintegrasikan sesuai spesifikasi.
- Jaminan kualitas dan pengujian:
- Pengujian tekanan hidrostatik atau pneumatik memverifikasi integritas tangki.
- Verifikasi pembersihan dan pengujian kebocoran dapat dilakukan untuk memastikan kompatibilitas CIP.
- Pengemasan dan pengiriman:
- Tangki disiapkan untuk pengiriman dengan kemasan pelindung yang sesuai, dan manual pemasangan menyertai unit yang dikirim.
Sektor kinerja dan aplikasi
- Makanan dan minuman:
- Bejana penyimpanan, fermentasi, dan pencampuran yang memerlukan desain higienis, kemudahan pembersihan, dan kompatibilitas dengan bahan pembersih kelas makanan.
- Produk susu dan turunan susu:
- Hasil akhir ultra-bersih, sanitasi, dan kontrol suhu yang tepat untuk pengolahan susu, keju, dan produksi yogurt.
- Farmasi dan biotek:
- Tangki yang kompatibel dengan ruang bersih yang memenuhi standar sanitasi yang ketat, persyaratan validasi, dan kemudahan pembersihan.
- Kosmetik dan perawatan pribadi:
- Tangki untuk pemrosesan batch, pencampuran resin, dan formulasi untuk meminimalkan kontaminasi.
- Pengolahan bahan kimia:
- Tangki tahan korosi untuk menangani bahan kimia kaustik atau agresif, dengan hasil akhir permukaan dan lapisan yang sesuai untuk peningkatan perlindungan.
- Pembuatan bir dan penyulingan:
- Tangki fermentasi dan bejana pematangan untuk kandungan alkohol ringan hingga tinggi, dengan agitasi dan kontrol suhu untuk pengembangan rasa.
Manfaat operasional dan pertimbangan siklus hidup
- Kebersihan dan keselamatan:
- Interior higienis mengurangi risiko kontaminasi, memungkinkan produksi barang konsumsi dan farmasi yang lebih aman.
- Efisiensi proses:
- Agitasi yang tepat dan optimalisasi transfer panas menghasilkan kualitas produk yang konsisten dan mengurangi waktu pemrosesan.
- Keandalan dan waktu kerja:
- Konstruksi las yang tahan lama meminimalkan risiko kebocoran dan waktu henti perawatan.
- Kemudahan pembersihan dan kesiapan CIP:
- Las yang halus, geometri melingkar, dan perincian gasket yang tepat mendukung prosedur CIP/SIP yang efektif.
- Umur panjang dan nilai jual kembali:
- Tangki baja tahan karat mempertahankan nilai lebih lama karena ketahanan korosi dan permintaan pasar untuk peralatan higienis.
Pemasangan, penugasan, dan pemeliharaan
- Perencanaan lokasi dan pemasangan:
- Tangki diposisikan untuk mengakomodasi tata letak perpipaan, sistem pembersihan di tempat, dan ruang untuk akses perawatan.
- Kesiapan CIP/SIP:
- Sistem pembersihan, nosel semprot, dan jalur drainase diintegrasikan untuk mendukung siklus sanitasi yang berulang.
- Kalibrasi dan validasi:
- Untuk aplikasi farmasi atau biotek, protokol validasi dapat mencakup IQ/OQ/PQ (Kualifikasi Pemasangan, Kualifikasi Operasional, Kualifikasi Kinerja) untuk mendokumentasikan pengoperasian yang tepat.
- Perawatan rutin:
- Inspeksi rutin terhadap lasan, gasket, fitting, dan isolasi memastikan kinerja berkelanjutan.
- Perlindungan permukaan dan pemantauan korosi membantu mendeteksi tanda-tanda degradasi dini.
- Suku cadang dan layanan:
- Akses ke gasket, segel, dan fitting yang kompatibel dengan penggantian langsung mengurangi waktu henti.
Studi kasus: menunjukkan dampak dalam pengaturan dunia nyata
- Air kota dan air limbah:
- Tangki baja skala besar mendukung penyimpanan dan pemrosesan di fasilitas pengolahan, dengan desain higienis yang tahan terhadap rezim pembersihan yang agresif.
- Produsen makanan dan minuman:
- Pabrik bir dan pabrik susu mengandalkan tangki baja tahan karat las untuk fermentasi dan penyimpanan, mencapai kualitas produk yang konsisten dengan pembersihan yang berulang.
- Manufaktur farmasi:
- Tangki yang kompatibel dengan ruang bersih memastikan pemrosesan aseptik, memenuhi harapan peraturan yang ketat dan persyaratan validasi.
Jaminan kualitas dan standar
- Sertifikasi material:
- Kelas baja tahan karat, hasil akhir permukaan, dan prosedur pengelasan harus disertifikasi untuk lingkungan penggunaan akhir.
- Kualitas manufaktur:
- QMS yang kuat memastikan penelusuran material, pengerjaan, dan hasil pengujian akhir.
- Verifikasi pihak ketiga:
- Inspeksi independen memverifikasi kesesuaian dengan spesifikasi klien dan standar industri.
Keberlanjutan dan pertimbangan lingkungan
- Daur ulang:
- Baja tahan karat sangat dapat didaur ulang, berkontribusi pada tujuan keberlanjutan siklus hidup.
- Produksi bersih:
- Desain higienis meminimalkan limbah dan mengurangi konsumsi bahan pembersih melalui sistem CIP yang efisien.
- Efisiensi energi:
- Permukaan transfer panas dan isolasi yang efisien mengurangi penggunaan energi dalam proses yang dikontrol suhu.
Arah masa depan dalam tangki baja tahan karat las
- Kembaran digital dan perawatan cerdas:
- Mengintegrasikan sensor dan model kembaran digital memungkinkan perawatan prediktif dan optimalisasi proses waktu nyata.
- Teknologi permukaan canggih:
- Interior hibrida atau berlapis nano mengurangi keausan, mempermudah pembersihan, dan meningkatkan ketahanan terhadap pewarnaan.
- Desain modular dan fleksibel:
- Komponen plug-and-play memungkinkan retrofit yang lebih cepat dan penskalaan ke kebutuhan produksi yang berubah.
- Desain yang didorong oleh keberlanjutan:
- Optimalisasi material dan pertimbangan akhir masa pakai akan terus membentuk pilihan desain tangki.
Tangki baja tahan karat las berdiri sebagai landasan dari pemrosesan industri modern. Mereka memberikan kebersihan, daya tahan, dan kemampuan beradaptasi di berbagai sektor, selaras dengan tuntutan ketat lingkungan produksi saat ini. Keahlian Center Enamel dalam merancang, membuat, dan mengirimkan tangki baja tahan karat las memastikan klien menerima bejana yang memenuhi standar sanitasi yang tepat, persyaratan operasional, dan nilai jangka panjang.